[Coding038] LeetCode 138
Copy List with Random Pointer
Get the knowledge flowing and circulating! :)
目录
※ 本题收获
本题的求解过程将会增强对链表中节点之间的顺序的把握!
具有十分重要的训练意义!
题目:138. Copy List with Random Pointer
A linked list of length n is given such that each node contains an additional random pointer, which could point to any node in the list, or null.
Construct a deep copy of the list. The deep copy should consist of exactly n brand new nodes, where each new node has its value set to the value of its corresponding original node. Both the next and random pointer of the new nodes should point to new nodes in the copied list such that the pointers in the original list and copied list represent the same list state. None of the pointers in the new list should point to nodes in the original list.
For example, if there are two nodes X and Y in the original list, where X.random --> Y, then for the corresponding two nodes x and y in the copied list, x.random --> y.
Return the head of the copied linked list.
The linked list is represented in the input/output as a list of n nodes. Each node is represented as a pair of [val, random_index] where:
val: an integer representingNode.valrandom_index: the index of the node (range from0ton-1) that therandompointer points to, ornullif it does not point to any node.
Your code will only be given the head of the original linked list.
Example 1:
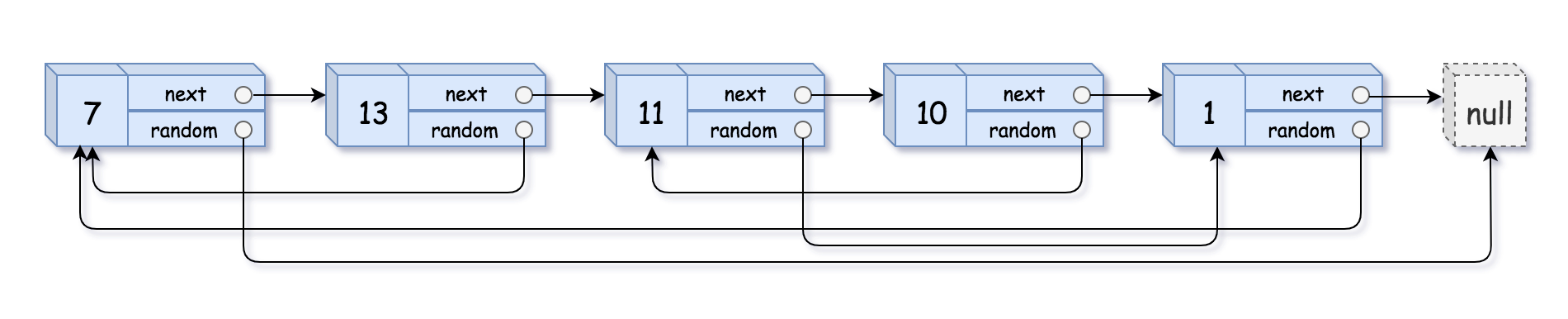
xxxxxxxxxx21Input: head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]2Output: [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
Example 2:
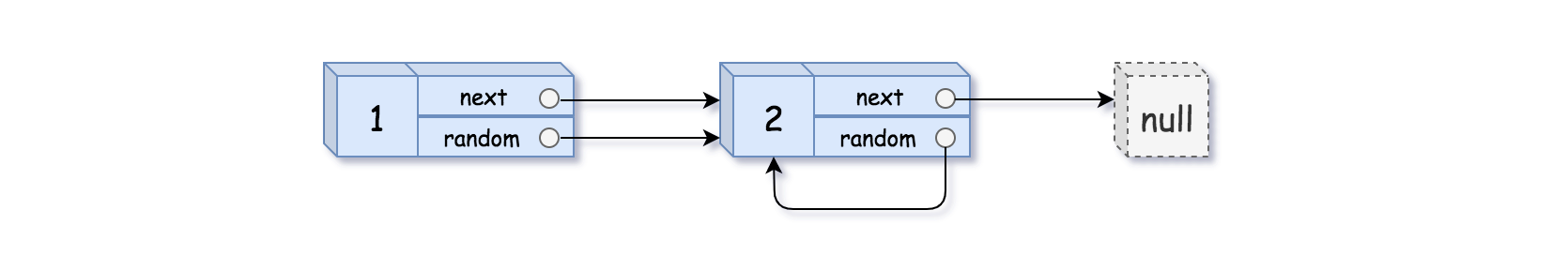
xxxxxxxxxx21Input: head = [[1,1],[2,1]]2Output: [[1,1],[2,1]]
Example 3:
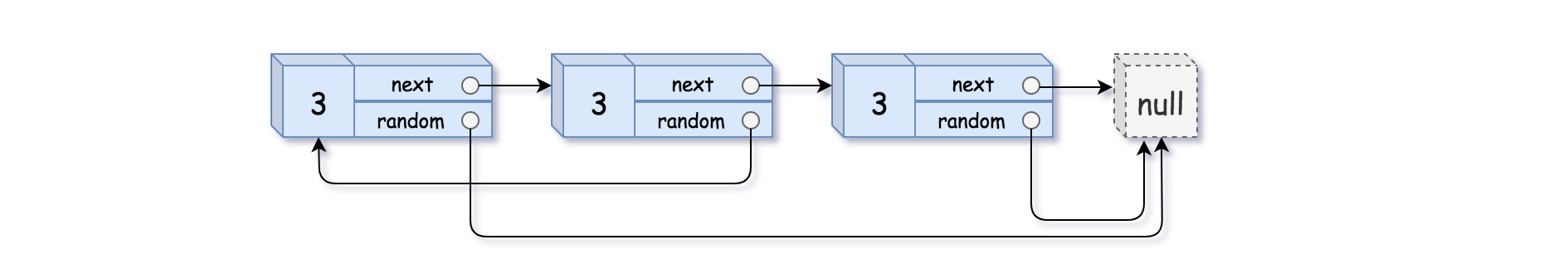
xxxxxxxxxx21Input: head = [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]2Output: [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
Constraints:
0 <= n <= 1000-104 <= Node.val <= 104Node.randomisnullor is pointing to some node in the linked list.
代码1(配 · 手绘过程图)
xxxxxxxxxx561/*2// Definition for a Node.3class Node {4 int val;5 Node next;6 Node random;7
8 public Node(int val) {9 this.val = val;10 this.next = null;11 this.random = null;12 }13}14*/15
16class Solution {17 public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {18 Node temp = head;19 while (temp != null)20 {21 Node newNode = new Node(temp.val);22 newNode.next = temp.next;23 temp.next = newNode;24 temp = temp.next.next;25 }26
27 Node itr = head;28 while (itr != null)29 {30 if (itr.random != null)31 {32 // itr.next实际上就是itr(副本)33 // itr.random.next实际上就是itr.random(副本)34 itr.next.random = itr.random.next;35 }36
37 itr = itr.next.next;38 }39
40 Node dummy = new Node(0);41 itr = head;42 temp = dummy;43
44 Node fast;45 while (itr != null)46 {47 fast = itr.next.next; // 原序列中的第二个Node48 temp.next = itr.next; // dummy后面跟上新序列的第1个Node49 itr.next = fast; // 恢复原序列的链接次序50 temp = temp.next; // 继续处理新序列的下一个序列51 itr = fast; // 按序(继续)处理原序列52 }53
54 return dummy.next;55 }56}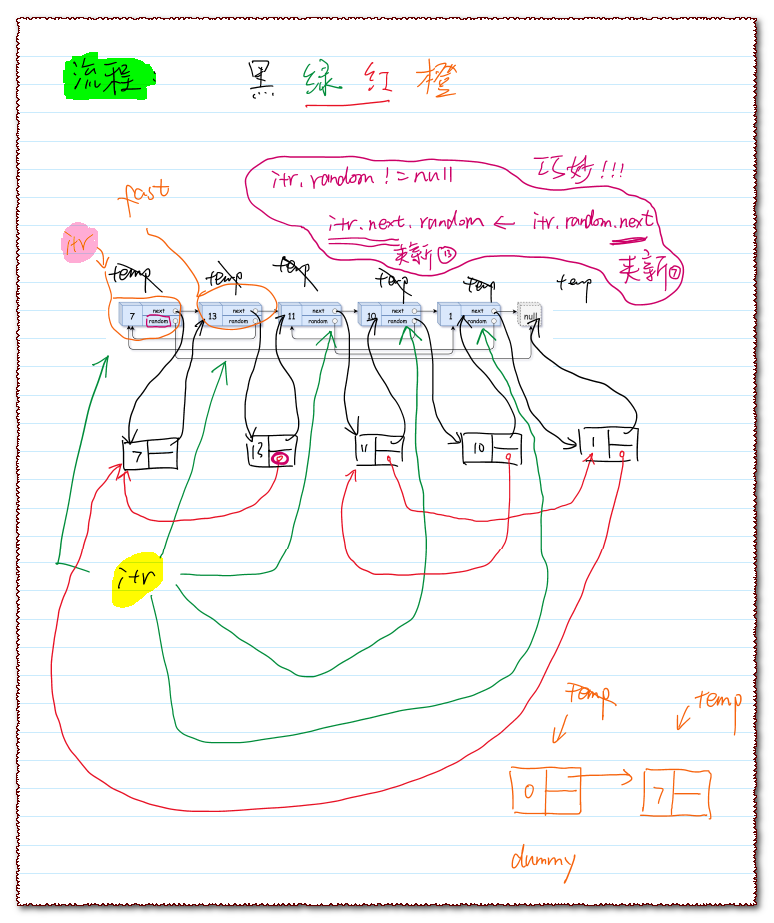
代码解读 | 评价
代码的执行流程:
先看黑色字体部分:在原有的序列相邻的Node之间,新增一个Node(value和前一个Node一样);
再看绿色字体部分:把副本相连起来(非常巧妙 @line34);
然后红色字体部分;
最后橙色字体部分:把原有序列衔接起来 & 把新序列串起来。
复杂度分析